DataHub Flow List
The DataHub Flow List page presents an overview of all configured data flows in your system. Adjust the default filter for Generic (Flows used by all 3PL customers) or Only Customer. Each row represents a single flow and displays information about its setup, involved parties, and transaction activity. The most important fields you will see here include:
- Number of Transactions – Shows how many transactions have been processed through the flow. Clicking this number opens a detailed list of the individual transactions.
- External Party Name – Indicates the external organization or system that receives or sends data for this flow.
- Bill-To Company Name – Displays the internal or external company responsible for billing associated with this flow.
- Type – Shows the protocol or mechanism (e.g., HTTP, SFTP, POP3) used to transfer data.
- Message Type – Describes the type or format of messages (e.g., JSON, XML) being transferred.
- Invoice Category – Indicates how invoices or billing information are categorized in this flow.
- Description – Provides a brief overview or purpose of the flow.
By reviewing these fields at a glance, you can quickly gauge which flows are active, how much data they handle, and who is responsible for them. For further analysis, simply click the Number of Transactions to drill down into the details of each transaction associated with that flow.
Edit Flow
You can click the EDIT in the record or click Edit in the top bar to open the Flow itself. The flow itself is an overview of the configured steps related to your integration process.
Note
Please be aware that changing your Flow might lead to disruption of your Business Process. Boltrics is not responsible for any disruptions caused by changes made by 3PL end users. Review the change log to revert back any changes that may cause disruptions.
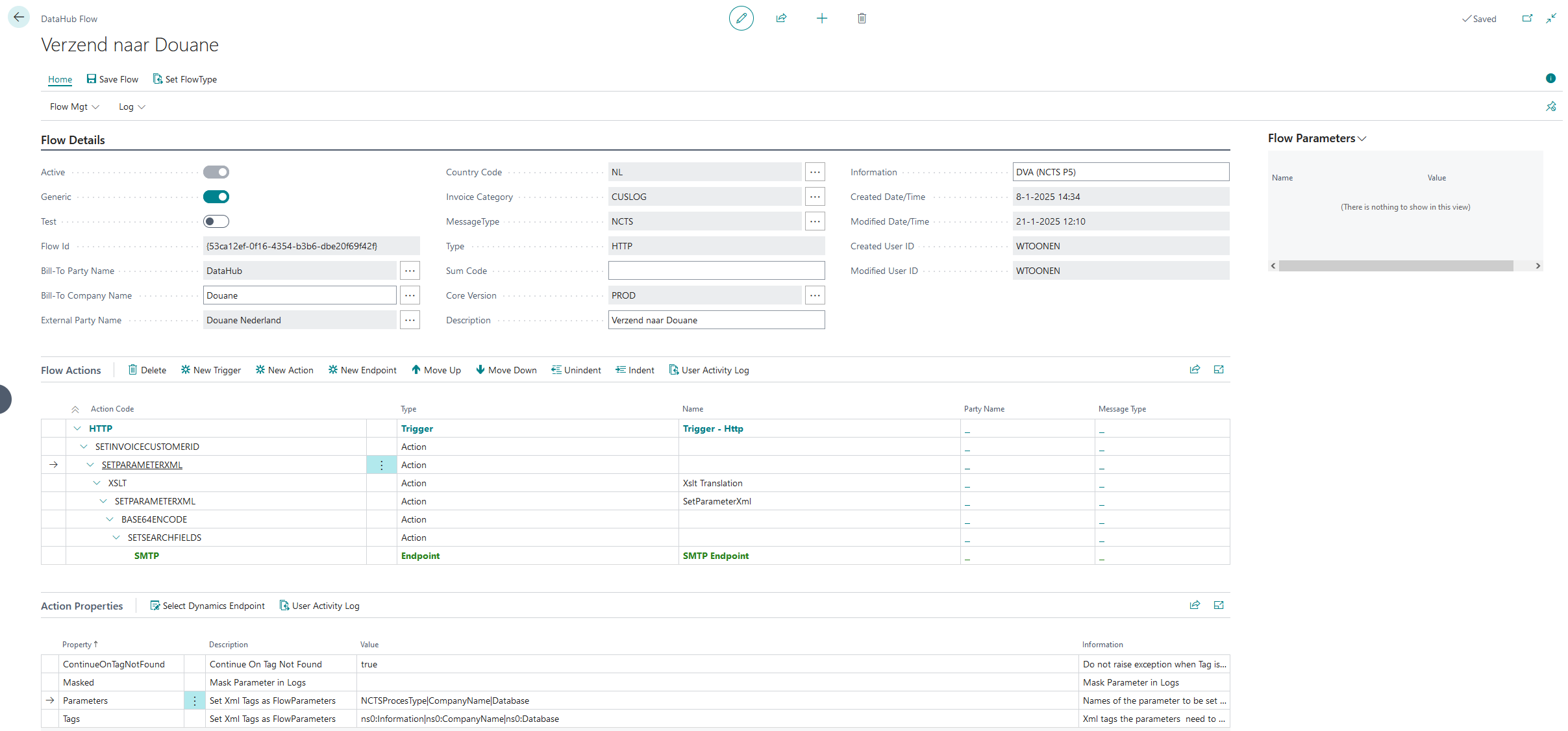
The DataHub Flow page appears after editing a DataHub Flow. A Flow always contains at least a Trigger, that initiates the execution of the flow, and an Endpoint that ends the execution of a Flow. One or more Actions are added to modify your data or retrieve data from external sources to influence the behavior of a flow. Here you will see an overview of a Generic Flow for Customs. You can always revisit this page yourself in 3PL Dynamics.
Flow Details
The Flow Details section provides general information about the current DataHub Flow, including the Flow ID, Bill-To Party, External Party, Message Type, and other high-level parameters. This area helps you understand the overall purpose and configuration of the flow at a glance.
Flow Actions
The Flow Actions section outlines the sequence of Triggers, Actions, and Endpoints that define how data is processed. A Trigger indicates the starting point or condition for the flow, an Action performs a specific processing step (like setting parameters or transforming data), and an Endpoint specifies the final destination or service that handles the data.
Action Properties
The Action Properties section lists detailed settings for each Trigger, Action, or Endpoint in the flow. Here, you can configure individual parameters, decide how data is masked or transformed, and determine the behavior of each processing step to ensure that the flow meets your business requirements.
Trigger Overview
This table contains a list of the Triggers and a brief explanation of their purpose.
| TRIGGER Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| HTTP | Starts the flow when an incoming HTTP request is received. Useful for inbound data from external services. |
| CALLBACK | Waits for a callback endpoint request, then returns a direct HTTP response. Ideal for asynchronous flows where another system “calls back” with data or status updates. |
| FTP | Initiates the flow when new files appear on an FTP server. Helps automate file pickup and subsequent processing. |
| SFTP | Similar to FTP but uses secure FTP. Begins the flow when new files arrive at the specified SFTP location. |
| POP3 | Monitors a mailbox using POP3. When new emails are found, the flow triggers and processes the message or attachments. |
| AFS | Triggers the flow based on Azure File Storage events, enabling automatic handling of files added or updated in Azure Files. |
| SCHEDULE | Initiates the flow according to a specified schedule or interval, allowing time-based automation (e.g., nightly or hourly tasks). |
Action Overview
This table contains a list of the most regularly used Actions and a brief explanation of their purpose.
| ACTION Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| REPLACE | Replaces specified text or patterns in the message or parameters with new values. This is useful for adjusting data before further processing. |
| XSLT | Performs an XSLT transformation on XML data, allowing you to convert or reshape the message into a different XML structure as required by downstream systems. |
| CONDITION | Evaluates certain conditions (e.g., checking values in the message) to decide which path the flow should take—enabling branching logic based on data content. |
| SETPARAMETERXML | Extracts specific XML tags from the message and sets them as Flow Parameters for use by subsequent actions. |
| SETPARAMETERJSON | Extracts specific JSON fields from the message and sets them as Flow Parameters for use by subsequent actions. |
| SETPARAMETERGUID | Generates or sets a GUID (unique identifier) as a Flow Parameter, often used for correlation or tracking. |
| SETPARAMETERDATETIME | Inserts or updates a date/time value as a Flow Parameter—useful for timestamps, scheduling, or logging. |
| REMOVENAMESPACES | Strips namespaces from an XML document, simplifying processing or comparison of XML elements later in the flow. |
| SLEEP | Pauses the flow for a defined number of milliseconds, allowing you to wait before continuing to the next action. |
| SPLITXML | Splits the XML message based on a specified XML tag or XML path, creating multiple smaller messages or records. |
| CONVERTJSON2XML | Takes a JSON payload and converts it into an XML structure, easing integration with systems that require XML. |
| CONVERTXML2JSON | Transforms an XML document into JSON format, useful for consuming XML data in JSON-based applications or APIs. |
| CONVERTPDF2XML | Extracts text from a PDF using Azure AI Document Intelligence and generates an XML structure for further use or analysis. |
| PLACEBETWEENTAGS | Inserts the incoming message between specified XML tags, providing a quick way to wrap raw data in a structured envelope. |
| BASE64DECODE | Decodes a Base64-encoded message back to its original binary or text format, making it available for further actions. |
| SETSEARCHFIELDS | Adds data to predefined Search Fields (1..10), often used for indexing, logging, or advanced searching in subsequent steps. |
| BASE64ENCODE | Encodes a message (binary or text) into Base64 format, enabling safe transport in systems that require plain text. |
Endpoint Overview
This table contains a list of the Endpoints and a brief explanation of their purpose.
| ENDPOINT Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| HTTP | Posts the input message to an HTTP endpoint, typically used for sending data to a RESTful service or receiving a response from a web server. |
| FTP | Uploads the message as a file to an FTP server, facilitating legacy or basic file-based integrations. |
| SFTP | Similar to FTP but uses SSH encryption for secure file transfer; uploads the message as a file to an SFTP server. |
| AFS | Uploads the message as a file to Azure File Storage (AFS), a managed file-share service within Microsoft Azure. |
| SCANVIEW | Posts the message to 3PL Dynamics Scanview for scanning, indexing, or additional document-based processing. |
| CALLBACK | Sends the message as a callback (e.g., HTTP POST), often used in asynchronous or webhook-style integrations where another system must confirm receipt. |
| SMTP | Sends the message as an email through an SMTP server, allowing email-based integrations or notifications. |
| TERMINATE | Terminates the transaction or flow, signaling that no further processing is required for this message. |